© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
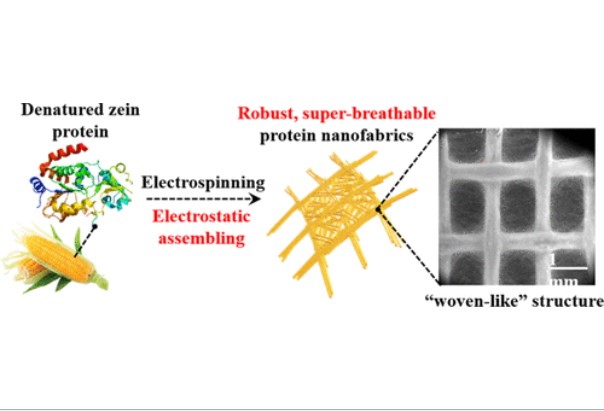
Nanofabrics made from abundant natural protein that possesses enormous amounts of functional groups may have important applications such as air filtration. However, protein nanofabrics with randomly distributed nanofibers have very low mechanical properties and high airflow resistance, both of which seriously reduce the breathability. Here, a super-breathable zein (corn protein) fabric having a unique "woven-like" nanofibrous structure (w-PNF) via the accumulation effect between the charged nanofibers and the collector during electrospinning is reported. The resulting w-PNF exhibits remarkable tensile strength and modulus, which are 3 and 9 times, respectively, higher than the random protein nanofibrous materials. The filtration tests indicate that w-PNF presents super-breathable performance, including ultralow airflow resistance (1/12 of that of the nonwoven nanofabric) and high filtration efficiency for capturing PM2.5 As compared with the reported nanofabrics, w-PNF maintains the same airflow resistance at up to 4 times higher airflow rate. In addition, w-PNF presents visible-light transparency (80%) and high resolution even in microareas. This work provides a significant strategy for designing and fabricating nanofabrics for boosting the development of biological nanomaterials.
由具有大量功能基团的丰富天然蛋白质制成的纳米织物可能具有重要的应用,例如空气过滤。然而,具有随机分布的纳米纤维的蛋白质纳米织物具有非常低的机械性能和高的气流阻力,这两者都严重降低了透气性。在此,报道了通过静电纺丝时带电的纳米纤维与集电体之间的累积作用而具有独特的“编织状”纳米纤维结构(w-PNF)的超透气玉米蛋白(玉米蛋白)织物。所得的w-PNF表现出显着的抗张强度和模量,分别比无规蛋白质纳米纤维材料高3倍和9倍。过滤测试表明,w-PNF具有超透气的性能,包括超低的气流阻力(非织造纳米织物的1/12)和用于捕获PM2.5的高过滤效率。与报道的纳米织物相比,w-PNF保持了透气性。相同的气流阻力,最高可达4倍的气流速率。此外,w-PNF即使在微区域中也具有可见光透明度(80%)和高分辨率。这项工作为设计和制造纳米织物以促进生物纳米材料的发展提供了重要的策略。
Published: 2020
Journal :ACS APPLIED BIO MATERIALS
Impact Factor:There is no data at this time
Paper link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsabm.0c00008