© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
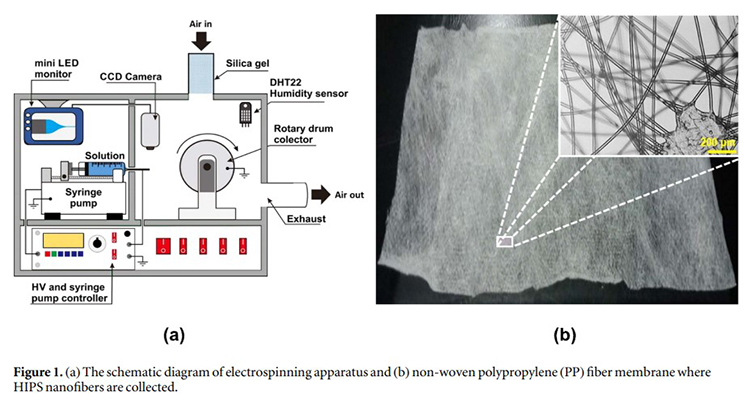
Nanofiber membranes were synthesized from waste high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) using electro-spinning method and then applied as air filtration media. The waste HIPS precursor solution with the concentration of 20 wt.% was prepared by dissolving waste HIPS into the mixture of d-limonene and DMF solvents. Beaded or fine nanofibers could be achieved by adjusting the ratio of solvents mixture (d-limonene and DMF). Using the ratios of solvents (d-limonene:DMF) of 3:1, 1:1, and 1:3, it was obtained beaded HIPS nanofibers with the average diameter of 272 nm, beaded HIPS nanofibers with the average diameter of 937, and fine HIPS nanofibers with the average diameter of 621 nm, respectively. From the FTIR spectral analysis, it was found that the FTIR peaks of the HIPS nanofiber membranes are the same as those of the cleaned waste HIPS and there are no FTIR peaks of DMF and d-limonene solvents. These findings implied that the electrospinning process allows the recycling of waste HIPS into HIPS nanofibers without any trapped solvent phases or apparent degradation of the original material. From the contact angle measurement, it was confirmed that the HIPS nanofiber membranes are hydrophobic and the presence of the beads in the HIPS nanofiber membranes varies their contact angles. From the air-filtration test, it was shown that the fiber morphology (beaded or fine nanofibers) considerably affects the filtration performance of the membranes. The presence of beads increased the distance between the fibers so that the pressure drop decreased. Moreover, the basis weight of the membrane greatly affected the filtration efficiency. The HIPS nanofiber membrane with the basis weight of 12.22 gm(-2) had the efficiency greater than 99.999%, which was equivalent to that of the HEPA filter.
利用静电纺丝法从废旧的高抗冲聚苯乙烯(HIPS)合成了纳米纤维膜,然后将其用作空气过滤介质。通过将废HIPS溶解在d-柠檬烯和DMF溶剂的混合物中来制备浓度为20 wt。%的废HIPS前体溶液。可以通过调节溶剂混合物(d-柠檬烯和DMF)的比例来获得微珠或细纳米纤维。使用溶剂(d-柠檬烯:DMF)的比例为3:1、1:1和1:3,可以得到平均直径为272 nm的珠状HIPS纳米纤维,平均直径为937的珠状HIPS纳米纤维,和平均直径分别为621 nm的HIPS纳米纤维。通过FTIR光谱分析,发现HIPS纳米纤维膜的FTIR峰与清洁的废HIPS的FTIR峰相同,并且没有DMF和d-柠檬烯溶剂的FTIR峰。这些发现表明,静电纺丝工艺可以将废HIPS回收到HIPS纳米纤维中,而不会捕获任何溶剂相或使原始材料明显降解。从接触角测量,证实了HIPS纳米纤维膜是疏水的,并且HIPS纳米纤维膜中珠的存在改变了它们的接触角。从空气过滤测试中可以看出,纤维的形态(微珠或细纳米纤维)会极大地影响膜的过滤性能。珠粒的存在增加了纤维之间的距离,从而降低了压降。而且,膜的基重极大地影响了过滤效率。单位面积重量为12.22 gm(-2)的HIPS纳米纤维膜的效率大于99.999%,相当于HEPA过滤器的效率。
Published: 2018
Journal :Materials Research Express
Impact Factor:1.914
Paper link: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2053-1591/aab6ef/meta