© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
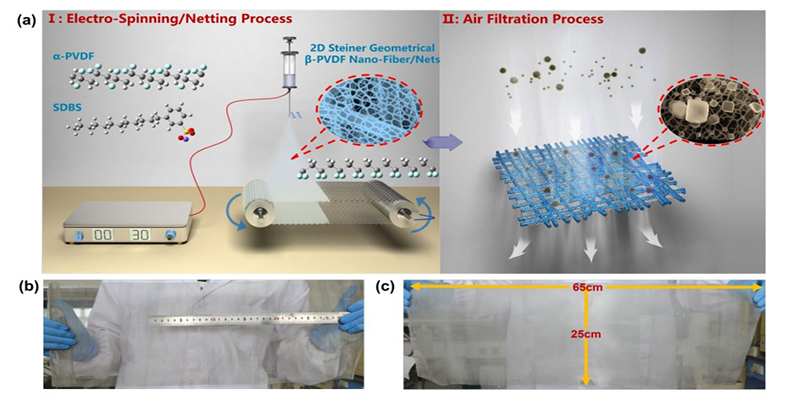
The emergence of Steiner minimal tree is of fundamental importance, and designing such geometric structure and developing its application have practical effect in material engineering and biomedicine. We used a cutting-edge nanotechnology, electrospinning/netting, to generate a Steiner geometrical poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) nanofiber/nanonet filter for removing airborne particulate matter (PM). Manipulation of surface morphologies by precise control of charged situation enabled the creation of two-dimensional nanonets with Steiner geometry. A significant crystalline phase transition of PVDF from alpha-phase to beta-phase was triggered by the dipole orientation and the intermolecular interactions derived from the electrostatic potential analysis. Particularly, the synergy of electrical interaction (ion dipole and dipole dipole) and hydrophobic interaction facilitated the formation of Steiner geometric structure during the evolution process of nanonets. The resultant PVDF nanofiber/nanonet air filter exhibited high filtration efficiency of 99.985% and low pressure drop of 66.7 Pa under the airflow velocity of 32 L/min for PM0.26 removal by the safest physical sieving mechanism. Furthermore, such filter possessed robust structure integrity for reusability, comparable optical transmittance, superior thermal stability, and prominent purification capacity for smoke PM2.5. The successful construction of such fascinating Steiner geometrical PVDF nanonets will provide new insights into the design and exploitation of novel filter media for air cleaning and haze treatment.
Steiner最小树的出现具有根本的重要性,设计这种几何结构并开发其应用在材料工程和生物医学中具有实际效果。我们使用了一种尖端的纳米技术,即静电纺丝/拉网,以产生一种Steiner几何聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)纳米纤维/纳米纤维过滤器,以去除空气中的颗粒物(PM)。通过精确控制带电情况来操纵表面形态,可以创建具有Steiner几何形状的二维纳米网。偶极子取向和静电势分析得出的分子间相互作用触发了PVDF从α相到β相的明显结晶相变。特别地,电相互作用(离子偶极和偶极偶极)和疏水相互作用的协同作用促进了纳米网进化过程中斯坦纳几何结构的形成。所得的PVDF纳米纤维/纳米空气过滤器在32 L / min的气流速度下通过最安全的物理筛分机制去除PM0.26时,过滤效率高达99.985%,低压降为66.7 Pa。此外,这种过滤器具有坚固的结构完整性,可重复使用,具有相当的透光率,具有出色的热稳定性,并具有出色的烟雾PM2.5净化能力。这种引人入胜的Steiner几何PVDF纳米网的成功构建,将为空气净化和雾度处理的新型过滤介质的设计和开发提供新见解。
Published: 2018
Journal :ACS Applied Materials & InterfacesImpact
Factor:9.002
Paper link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.8b16564