© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
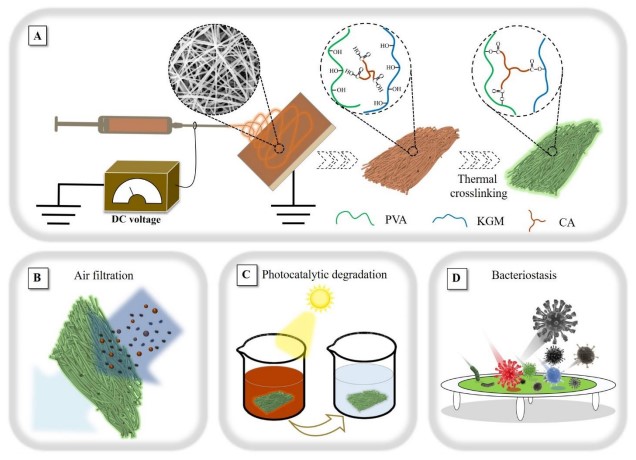
Ambient particulate matter pollution has posed serious threats to global environment and public health. However, highly efficient filtration of submicron particles, the so-named "secondary pollution" caused by, e.g., bacterial growth in filters and the use of nondegradable filter materials, remains a serious challenge. In this study, poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and konjac glucomannan (KGM)-based nanofiber membranes, loaded with ZnO nanoparticles, were prepared through green electrospinning and ecofriendly thermal cross-linking. Thus obtained fibrous membranes not only show highly efficient air-filtration performance but also show superior photocatalytic activity and antibacterial activity. The filtration efficiency of the ZnO@PVA/KGM membranes for ultrafine-particles (300 nm) was higher than 99.99%, being superior to that of commercial HEPA filters. By virtue of the high photocatalytic activity, methyl orange was efficiently decolorized with a removal efficiency of more than 98% at an initial concentration of 20 mg under 120 min of solar irradiation. A multifunctional membrane with high removal efficiency, low flow resistance, superior photocatalytic activity, and superior antibacterial activity was successfully achieved. It is conceivable that the combination of a biodegradable polymer and an active metal particle would form an unprecedented photocatalytic system, which will be quite promising for environmental remediation such as air filtration and water treatment.
环境颗粒物污染对全球环境和公共健康构成了严重威胁。然而,亚微米颗粒的高效过滤,所谓的“二次污染”是由例如过滤器中的细菌生长和使用不可降解的过滤材料引起的,仍然是一个严峻的挑战。在这项研究中,通过绿色静电纺丝和环保的热交联制备了聚乙烯醇(PVA)和魔芋葡甘露聚糖(KGM)基纳米纤维膜,其中负载了ZnO纳米颗粒。如此获得的纤维膜不仅显示出高效的空气过滤性能,而且显示出优异的光催化活性和抗菌活性。 ZnO @ PVA / KGM膜对超细颗粒(300 nm)的过滤效率高于99.99%,优于商用HEPA过滤器。凭借高的光催化活性,甲基橙在120分钟的太阳辐射下以20 mg的初始浓度有效脱色,去除效率超过98%。成功地获得了具有高去除效率,低流动阻力,优异的光催化活性和优异的抗菌活性的多功能膜。可以想象,可生物降解的聚合物和活性金属颗粒的结合将形成前所未有的光催化体系,这对于诸如空气过滤和水处理之类的环境修复将是非常有应用前景的。
Published: 2019
Journal :ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES
Impact Factor:9.002
Paper link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.9b01508