© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
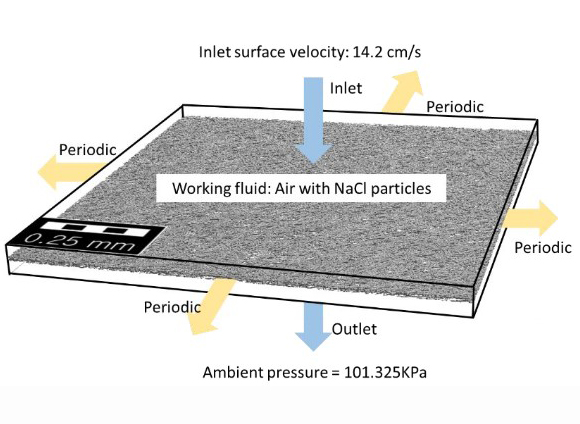
The buildup of pressure drop with mass loading of particles aggravates the breathing resistance and energy consumption of filters. This study investigated the role of intra- and interlayer space of filter media on the pressure drop development with continued particle loading. Five basic morphologies, including microfibers, nanofibers, microbeads-on-strings, and a mix of those morphologies were fabricated via electrospinning. Then the variations of layered constructions were made, to include a total 14 different filter structures. For a single layer filter media, the pore size rather than the percent porosity had a major impact on the pressure drop. For dual layers, the space between the layers and the placement order of webs were important factors affecting the pressure drop and depth loading of particles. Computational modeling was used to interpret the role of the interlayer space on the pressure drop, by monitoring the air flow and particle movement within the filter constructions, where the computational prediction corresponded to the tendency of the experimental findings. The novelty of this study lies in the combined approach of the experimental and computational work to understand the particle capture phenomenon during the mass loading.
压降随着颗粒的质量负载而增加,加剧了过滤器的呼吸阻力和能量消耗。这项研究调查了滤料的层间和层间空间在持续颗粒负载下压降发展中的作用。通过静电纺丝制造了五种基本形态,包括超细纤维,纳米纤维,串珠微珠以及这些形态的混合。然后,进行分层构造的变化,以包括总共14种不同的过滤器结构。对于单层过滤器介质,孔径而不是孔隙率百分比对压降有重大影响。对于双层,层之间的空间和网的放置顺序是影响颗粒的压降和深度负荷的重要因素。通过监视过滤器结构中的气流和颗粒运动,使用计算模型来解释中间层空间对压降的作用,其中计算预测与实验结果的趋势相对应。这项研究的新颖之处在于通过实验和计算工作相结合的方法来了解质量加载过程中的颗粒捕获现象。
Published: 2020
Journal :ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
Impact Factor:9.002
Paper lin:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.0c14958