© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
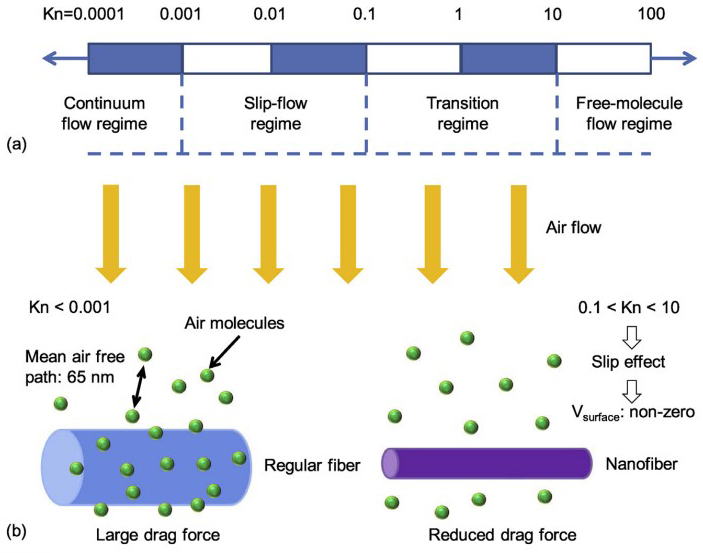
Electrospun nanofiber air filters can achieve high PM2.5 removal efficiency with a relatively low pressure drop because of the slip effect. They may therefore be applied in buildings to reduce indoor exposure to PM2.5 with lower energy consumption. This study first fabricated 25 nylon nanofiber filters with different filter parameters of fiber diameter, filter thickness, and packing density. The pressure drop across each nanofiber filter was measured under five different face velocities. This study then developed a method for modeling the pressure drop across electrospun nanofiber air filters using the filter parameters. 125 sets of experimental data were obtained for the model development, and a semi-empirical model was developed to predict the pressure drop across nylon electrospun nanofiber filters. The results showed that the pressure drop was proportional to the face velocity and filter thickness. The product of drag coefficient and Reynolds number was a function of both packing density and Knudsen number. The semi-empirical model reasonably predicted the pressure drop across the nylon electrospun nanofiber filters with a median relative error of 4.3%.
电纺纳米纤维空气过滤器由于滑移效应,可以在相对较低的压降下实现较高的PM2.5去除效率。因此,它们可用于建筑物中,以降低室内PM2.5的暴露,并降低能耗。本研究首先制造了25种尼龙纳米纤维过滤器,它们具有不同的过滤器参数,包括纤维直径,过滤器厚度和堆积密度。在五种不同的表面速度下测量了跨每个纳米纤维过滤器的压降。然后,这项研究开发了一种使用过滤器参数对电纺纳米纤维空气过滤器上的压降建模的方法。获得了125套用于模型开发的实验数据,并开发了一个半经验模型来预测尼龙电纺纳米纤维过滤器上的压降。结果表明,压降与表面速度和过滤器厚度成正比。阻力系数和雷诺数的乘积是堆积密度和克努森数的函数。半经验模型可以合理地预测尼龙电纺纳米纤维过滤器上的压降,中位相对误差为4.3%。
Published: 2018
Journal :BUILDING AND ENVIRONMENT
Impact Factor:5.847
Paper link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360132318303640