© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
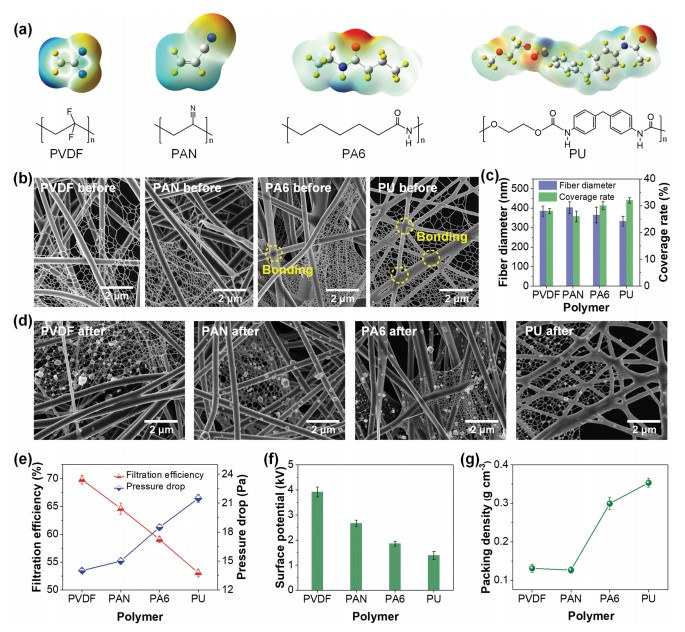
Particulate matter (PM) pollution in air is thought to be an important mortality risk factor globally. Most existing air filters face the extreme challenge of effectively removing PM0.3, which has the most penetration particle size (MPPS) of approximate to 0.3 mu m yet is particularly harmful. Here, an innovative in situ electret electrospinning/netting technique that can manipulate both solution phase separation and crystal phase transition is reported to develop self-polarized polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiber/net membranes with 2D networks and superior surface adhesion. By combining the true nanoscale diameter (approximate to 21 nm), small pore size (approximate to 0.26 mu m), and highly electret surface (6.8 kV potential) of the 2D nanonets, the synergistic effect of sieving and adhesion for MPPS PM0.3 is achieved. Such double capture characteristic enables the high-efficiency (approximate to 99.998%) capture of PM0.3 while maintaining low air resistance (approximate to 0.1% atmosphere pressure). Moreover, the nanofiber/net filters show integrated properties of superhydrophobicity, desirable transparency (91%), and long-term stability. The synthesis of such attractive nanomaterials presents a promising attempt toward the development of high-performance filtration/separation materials for numerous applications.
空气中的颗粒物(PM)污染被认为是全球范围内重要的死亡风险因素。现有的大多数空气过滤器都面临着有效去除PM0.3的严峻挑战,PM0.3的最大渗透粒径(MPPS)约为0.3微米,但特别有害。在这里,据报道,一种创新的原位驻极体静电纺丝/结网技术可以同时控制溶液相分离和晶体相变,从而开发出具有2D网络和优异的表面附着力的自极化聚偏二氟乙烯纳米纤维/网膜。通过结合二维纳米网的真实纳米级直径(约21 nm),小孔径(约0.26μm)和驻极体表面(6.8 kV电位),对MPPS PM0.3的筛分和粘附具有协同作用已完成。这种双重捕获特性可实现高效(约99.998%)的PM0.3捕获,同时保持低空气阻力(约0.1%大气压)。而且,纳米纤维/网状过滤器显示出超疏水性,所需的透明度(91%)和长期稳定性的综合特性。这种有吸引力的纳米材料的合成为开发用于多种应用的高性能过滤/分离材料提出了有意义的尝试。
Published: 2020
Journal :ADVANCED FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS
Impact Factor:16.723
Paper link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adfm.201909554