© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
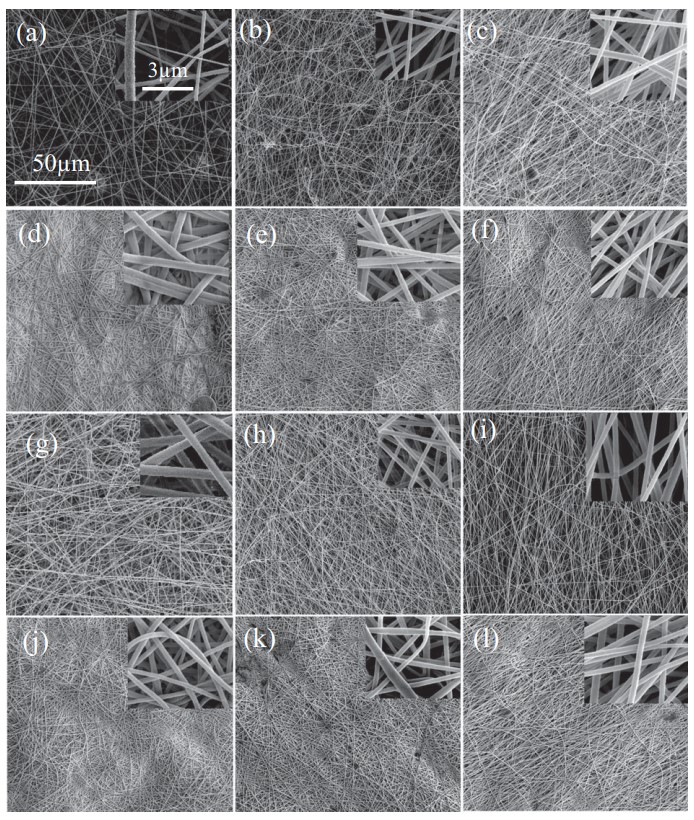
Electrospun nanofibrous membranes were engineered for aerosol particle removal by controlling the fiber density and alignment across electrospunmats. Electrospun nanofiber membranes were deposited on both, rotatory drum and stationary collectors, to investigate the effect of fiber alignment on filtration performance. Poly(acrylonitrile)/dimethyl formamide (PAN/DMF) solutions were used to produce membranes for applications in air purification. The air filtration performance of as-produced and hot-compacted membranes were systematically evaluated with regard to penetration, pressure drop, and quality factor when subjected to potassium chloride (KCl) aerosol particles in the size-range of 300 nm to 12 mu m. The membranes offered air filtration efficiencies in the range of 77.7% to 99.616% and quality factors between 0.0026 and 0.0204 (1/Pa). The samples were benchmarked against commercial filters and were found to exhibit similar quality factors but higher air filtration efficiencies. These results were correlated to differences in pore morphologies and fiber orientation distributions generated from the different processing techniques, which revealed that the alteration of the fiber density is an effective method for enhancing air filtration performance. (C) 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
通过控制纤维密度和跨电纺垫的排列,设计了电纺纳米纤维膜以去除气溶胶颗粒。将电纺纳米纤维膜沉积在旋转鼓和固定收集器上,以研究纤维排列对过滤性能的影响。聚(丙烯腈)/二甲基甲酰胺(PAN / DMF)溶液用于生产用于空气净化的膜。当对尺寸在300 nm至12μm范围内的氯化钾(KCl)气溶胶颗粒进行处理时,针对渗透性,压降和品质因数,系统地评估了制成膜和热压膜的空气过滤性能。该膜的空气过滤效率在77.7%至99.616%范围内,品质因数在0.0026至0.0204(1 / Pa)之间。样品以商用过滤器为基准,发现具有相似的品质因数,但空气过滤效率更高。这些结果与不同加工技术产生的孔隙形态和纤维取向分布的差异相关,这表明改变纤维密度是提高空气过滤性能的有效方法。 (C)2018 Elsevier B.V.保留所有权利。
Published:2018
Journal :SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
Impact Factor:7.137
Paper link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0048969717337750