© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
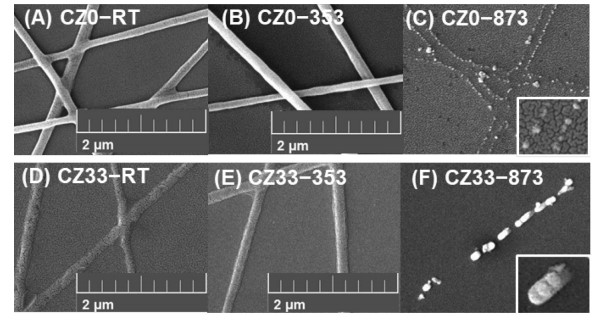
In this study, the physicochemical properties and antibacterial activity of copper-zinc (CuZn) nanofibers and nanoparticles were investigated by increasing zinc content in copper, which is known to have antibacterial properties. Copper and zinc nanofibers (CZ NFs) were prepared using the electrospinning method and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was used as a polymer to control the viscosity of the precursor solution (CuZn/PVP). The obtained nanofibers were categorized into two different groups. One group was calcined at 353 K in ambient and the other group at 873 K in Ar environment. These conditions were determined from TG/DTA results. CuZn nanofibers were obtained by removing the solvent and CuZn nanoparticles were obtained by decomposing the polymer. The structural and chemical properties of the fabricated nanofibers were studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). As a result of the antibacterial test, we were able to confirm that the nanofibers tend to exhibit stronger antibacterial effects than nanoparticles. In the case of Cu nanofibers, we observed that Zn(OH)(2) has a dominant effect on the antibacterial activity.
在这项研究中,通过增加铜的锌含量来研究铜锌(CuZn)纳米纤维和纳米颗粒的理化特性和抗菌活性,已知铜具有抗菌特性。使用静电纺丝方法制备了铜和锌纳米纤维(CZ NFs),并使用聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)作为聚合物来控制前体溶液(CuZn / PVP)的粘度。将获得的纳米纤维分为两个不同的组。一组在环境温度为353 K下煅烧,另一组在Ar环境下为873 K煅烧。这些条件是根据TG / DTA结果确定的。通过除去溶剂获得CuZn纳米纤维,并且通过分解聚合物获得CuZn纳米颗粒。使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM),X射线衍射(XRD)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)研究了制成的纳米纤维的结构和化学性质。抗菌测试的结果是,我们能够确认这种纳米纤维往往比传统的纳米纤维具有更强的抗菌作用。在铜纳米纤维的情况下,我们观察到Zn(OH)(2)对抗菌活性具有主要作用。
Published: 2020
Journal :APPLIED SURFACE SCIENCE
Impact Factor:6386
Paper link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0169433219337006