© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
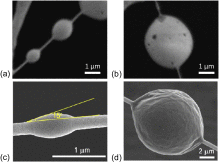
Nanofiber filter media can potentially reduce exposure to PM2.5 in indoor environments because of the filters' high particle-removal efficiency. To facilitate such filter use, this study conducted a series of experiments to understand the evolution of wetting liquid aerosols, taking incense particles as an example, on nanofiber filter media and the influence of this evolution on PM2.5 removal efficiency and pressure drop. Scanning electron microscope images were also taken to observe the nanoscale interactions between incense particles and the nanofiber network. The results show that the PM2.5 removal efficiency at first decreased as the loading mass increased, because interactions between the particles and the nanofiber network enlarged the pores. The evolution of pressure drop may consist of two stages, i.e., a first stage with a linear relationship, and a second stage with a steep increase in pressure drop with the loading mass. When the pore size became small enough, in addition to inertial impaction and Brownian diffusion, the capture mechanism of interception also became significant. Consequently, the second stage, with a steep increase, tended to occur. Finally, methods for establishing empirical equations for PM2.5 removal efficiency and pressure drop as a function of loading mass were proposed.
纳米纤维滤料可有效去除室内环境中的PM2.5,这是因为滤料的高效除尘效率。为了促进此类过滤器的使用,本研究进行了一系列实验,以了解润湿液体气溶胶在纳米纤维过滤介质上的演变,以熏香颗粒为例,以及这种演变对PM2.5去除效率和压降的影响。扫描电子显微镜图像也被用来观察香颗粒和纳米纤维网络之间的纳米级相互作用。结果表明,由于颗粒和纳米纤维网络之间的相互作用扩大了孔隙,因此PM2.5的去除效率首先随着负载量的增加而降低。压降的演变可以包括两个阶段,即,具有线性关系的第一阶段,和具有随负载质量而急剧下降的第二阶段。当孔径变得足够小时,除了惯性碰撞和布朗扩散,拦截的捕获机制也变得很重要。因此,倾向于发生急剧增加的第二阶段。最后,提出了建立PM2.5去除效率和压降随负载质量变化的经验方程的方法。
Published: 2020
Journal :BUILDING AND ENVIRONMENT
Impact Factor:5.847
Paper link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360132320300834