© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
In a study published in Scientific Reports, a unique functionalized nanofiber air filter (FNA) made up of polyvinyl alcohol, carbon nanoparticle, and tea leaf extract was created through an electrospinning process.
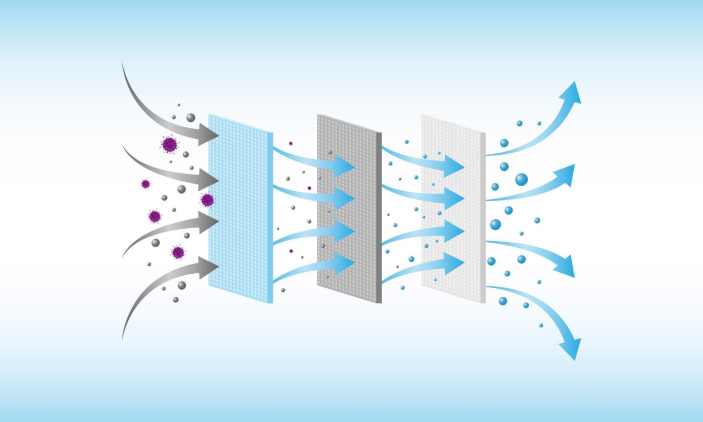
Electrospinning is a distinct process for creating nanoscale fibers with radii varying from microscale to nanoscale. Polymer-based electrospun substances with nanometer-sized particles are widely used in air filter systems. The substances are cytocompatible, reusable, washable, as well as lightweight.
The ambient air contains hazardous particulate matter (HPM) contaminants such as heavy metal dust, particles, poisonous gases, bacteria, fungi, and organic contaminants such as aerosolized particles, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and benzene.
Tiny particles having a radius less than 1.25 µm, pose a threat to human pulmonary function. Breathing them in increases the chances of cancerous, teratogenic, mutagenic consequences as well as pulmonary illnesses like asthma, lung cancer, and heart disease, and stroke.
Adequate protection from the sun requires a physical shield that absorbs or reflects ultraviolet rays before they make it to the skin's surface. Efforts have been concentrated on increasing the effectiveness of shielding against ultraviolet radiation in air filters.
Biological matter, like carbon in elemental and organic forms, along with inorganic substances, constitutes the particles of particular matter (PM) in the atmosphere. Various causes contribute to harmful atmospheric contamination, such as combustion of organic matter, pollutants from factories, soil dust, aerosols, and fossil fuel burning.
Chemical makeup, morphology, and mechanical properties all impact the behavior of particulate matter particles. An efficient air filter developed via electrospinning is a better solution for capturing different air contaminants. The kind of atmospheric contamination determines the air filter's performance, and the contaminant collection method may be altered accordingly.
Highly efficient particulate air filters and extremely low particulate air filters developed by electrospinning capture tiny PM with filtering performance of 98.98 percent and 98.99 percent, respectively.
Due to the presence of carboxyl and hydroxyl functional groups, tea leaf extract is utilized as an organic, inexpensive adsorbent for harmful metallic impurities. Canteens create tea leaf waste, which might be utilized for adsorption to extract heavy metals out of aqueous mixtures.
Tea leaf waste is a potential option due to its widespread accessibility, cheap cost, and efficient adsorption of harmful ions like Ni, Cr(VI), Cu, Pb, etc. The elimination of harmful metallic ions from the atmosphere employing agricultural debris is developing as an inexpensive approach to address the current system's limitations, which uses expensive chemicals.
Carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) have several properties that make them appealing candidates for a spectrum of uses. Their properties of being highly soluble and highly stable in a variety of usual solvents have resulted in the development of specific electrospinning-based air filter uses.
Among the most prevalent polymeric hydrophiles, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) has demonstrated excellent mechanical properties. It is a biologically compatible and degradable hydroxyl polymer with high chemical durability and flexibility that is employed in the production of specialized membrane technology.
These properties make electrospinning-based scaffolding an excellent substitute for air filter uses. Moreover, merging antibacterial carbon nanoparticles and tea leaf extract with PVA-based functionalized nanofiber air filter (FNA) increases their antimicrobial effectiveness and adsorption of airborne metallic particles.
In this study, the team produced electrospinning-based functionalized nanofiber air filters for PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 particle collection substances. Electrospun FNA has excellent mechanical, physicochemical, and antibacterial properties. An effectiveness assessment revealed that PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 collection was considerably higher in specimens of contaminated air.
The findings demonstrate that the developed PVA/CNPs/TLE nanoscale air filters outperform PVA/CNPs and PVA air filters in terms of particulate matter filtering. The produced air filter effectively removed PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 from contaminated air, demonstrating that it is a practical and inexpensive technique. These novel PVA/CNP/TLE nanoscale air filters may be found in a variety of industrial, home, and commercial settings.
Senthil, R., Sumathi, V., Tamilselvi, A., Kavukcu, S. B., & Aruni, A. W. (2022). Functionalized electrospun nanofibers for high efficiency removal of particulate matter. Scientific Reports, 12. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-12505-w
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.