© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
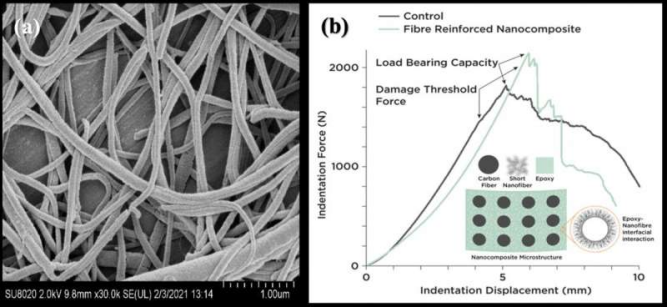
(a)Short nanofibers and (b) response of short nanofiber reinforced composite’s microstructure. Credit.....
Carbon fiber composites are preferred structural materials due to their high specific strength and modulus. Laminated construction of carbon composites and anisotropic nature, though, leave them sensitive to external loading. Since a brittle matrix controls the properties in and out of plane direction, interlaminar resin-rich regions are particularly susceptible to matrix cracking. Such incipient damage eventually evolves into life-limiting fracture, such as delamination under Mode II loading.
everal techniques have been employed to arrest crack genesis and propagation, thereby improving the damage resistance of composites. One of the most promising approaches is to modify epoxy with nanoparticles because of their high surface area to volume ratio and capability to counter micron scale cracks. However, nanoparticles are intricately associated with agglomeration in microstructure that can serve as embrittled damage initiation sites.
Electrospun short nylon 6 nanofibers (figure a) were proposed as an alternative epoxy reinforcement since their bulk mechanical properties were comparable to those of epoxy. High surface area and aspect ratio nanofibers were expected to introduce energy absorbing interfaces and nano-scale toughness mechanisms (figure b). Fabrication involved spinning and shortening of nanofibers followed by modification of epoxy to fabricate carbon fiber composite using vacuum bagging. Samples were tested under quasi-static indentation loading in accordance with ASTM D6264/D6264M-17.
Results showed an improvement of 8.7, 8.8, and 53% in peak force, displacement and elastic toughness at optimum nanofiber concentration. External directional damage growth was suppressed, and damage area increased marginally. At optimum nanofiber concentration, delaminated area reduced by 12.6%. Suppression of compressive fiber failure and enhanced interlaminar bonding were credited to offer superior performance.
These newly developed electrospun nanofiber-reinforced carbon composites attempt to address the classical issue of poor damage resistance of composites commonly reported in aerospace, marine and automotive applications. Improvement in damage resistance is likely to reduce non-destructive inspection's costs and adoption of composite structures with low safety factor.
"Carbon fiber composites is now well adopted in the aircraft and automobile industries due to its high specific strength and stiffness, enabling the aircraft and vehicles to be more fuel efficient and cost effective. However, accidents are bound to happen and when this occurs, repair can be costly in terms of materials and turn around time. Modifying the carbon fiber composite to become more impact resistance is key to mitigating the problem.
Article Source: https://phys.org/news/2023-03-electrospun-short-nylon-nanofibers-resistance.html