© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
Electrospinning is a process that involves the following:
· An inherently complex, multi-component material such as the polymer solution
· A fluidic and electrical equipment often including needles, syringes, and motorized elements for careful control of flow rates and generators providing high voltages
· The environment external to the process, which may range from air atmosphere to closed chambers operating with controlled gases or in stabilized temperature, vacuum conditions, etc.
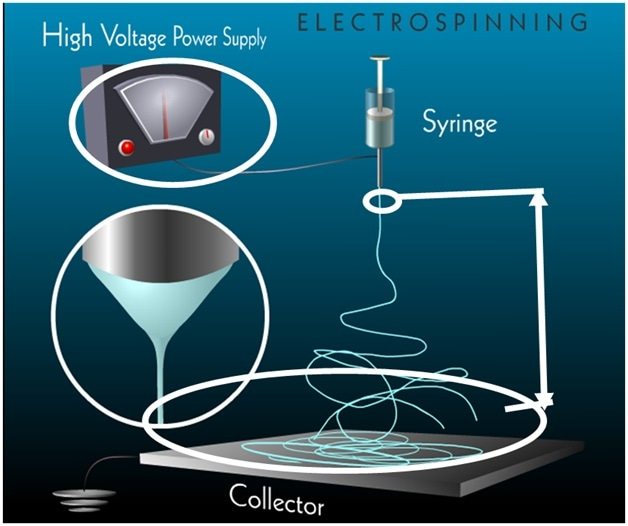
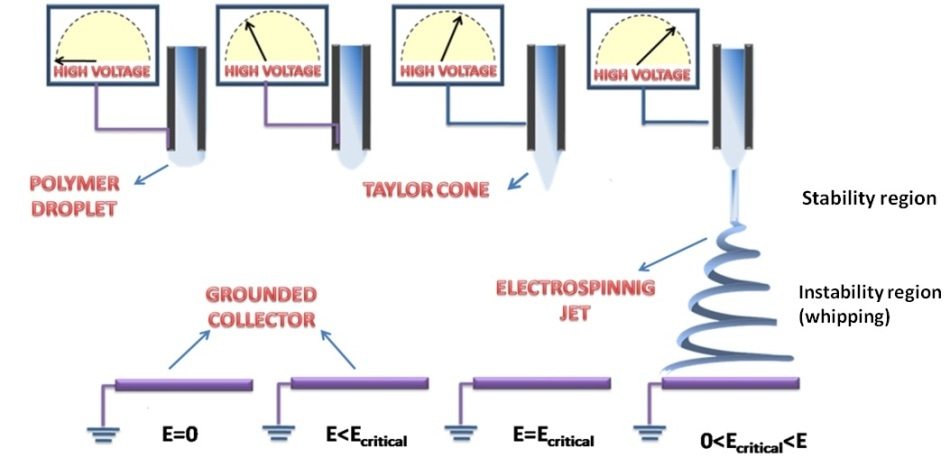
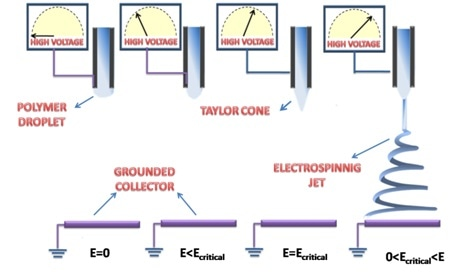
An automatic syringe pump is used to pump the fluid through a syringe. A voltage is supplied (using several kV potential) to positively charge the syringe needle. As shown in the below images, the resulting electric field causes fibers to be pulled out of the droplet at the end of the syringe tip and onto a grounded metal collector.
Solution parameters for the electrospinning process include solvent, solution temperature, additives, viscosity, concentration, surface tension, and molecular weight.
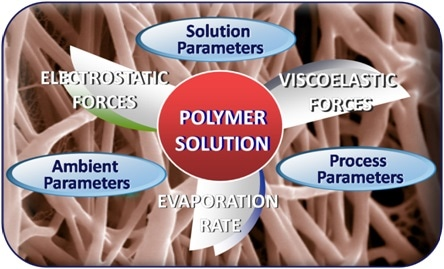
Process parameters of the electrospinning process include flow rate, polarity, spinneret geometry, needle to collector distance, and applied voltage.
Ambient parameters include humidity and temperature.
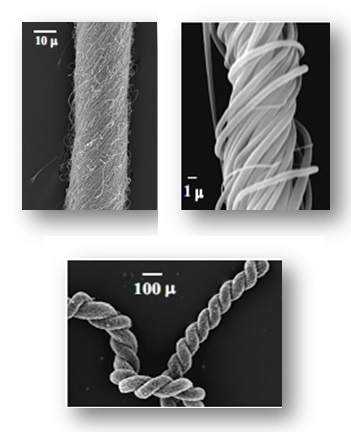
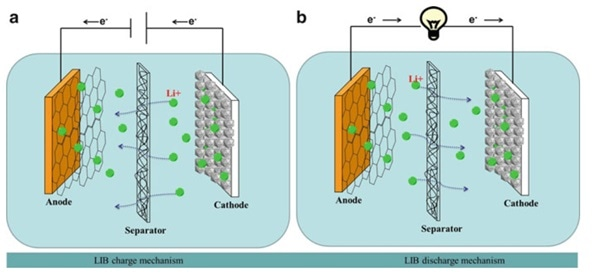
Electrospinning is an effective technology for the production of fibrous membrane with fiber diameter of several naonmeters to several micrometers. The electrospun fibrous membranes have advantages of high porosity, which, results in low cell resistance and high ionic conductivity. Consequently, the performance of electrospun fibrous membranes is better than the traditional microporous polyolefin membranes.
Nanofibers not only have many potential technical advantages but they are also easy and not expensive to produce. Due to these advantages, they have been the subject of intense research, particularly in the last two decades and have drawn the attention of many researchers from various fields.
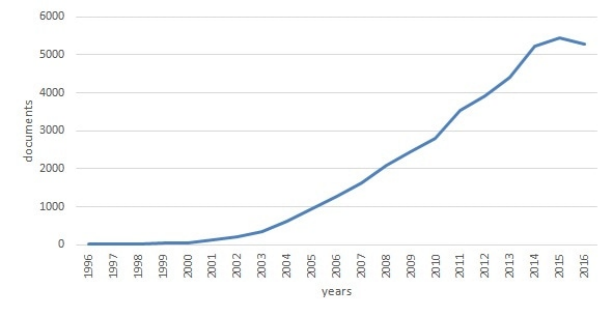
Documents published between 1996-2016 with “electrospinning or nanofibers” in “Title, Abstract, Keyword” parts in Scopus Database
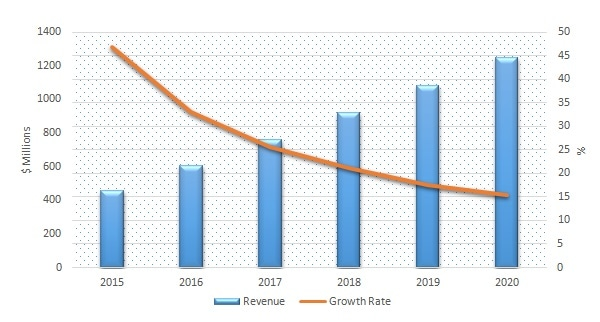
Global Nanoffiber Market 2015-2020, Technavio
The global nanofiber market was valued at $455 million in 2015 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 24.12% to reach 1.2 billion by 2020
The following are the advantages of nanofibers:
· High porosity (ca. 90%)
· High surface area (1 - 100 m2/g)
· Small diameters (10 nm - 10 mm)
· Small fiber-to-fiber distance

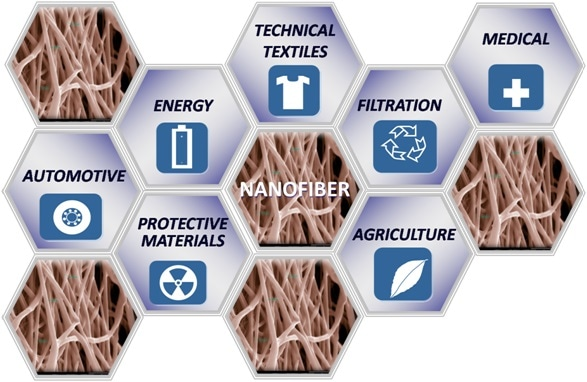
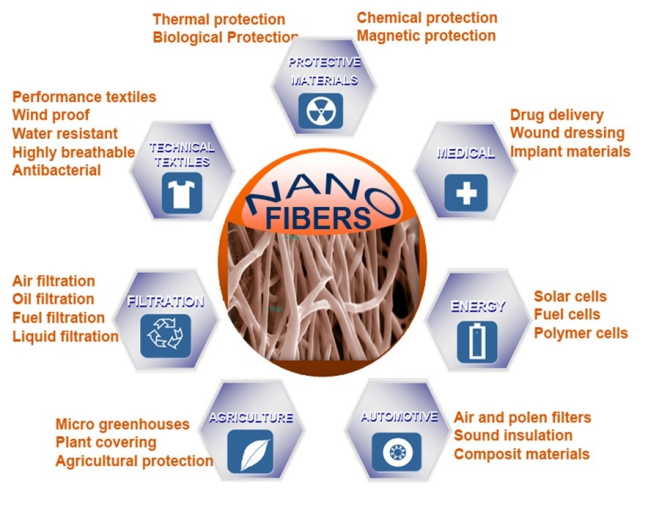
A nano mat is a breathable fabric, but its small size does not allow even bacteria to enter. These properties make nanofibers a potential candidate in a wide range of field applications like semiconductors, catalysts, filtration, fuel cells, scanning probe microscopy, optical waveguides, tissue repair, composites, and sensors in industries such as instrumentation, sensors, aerospace, automotive, energy, electronics, mechanical, and chemical.

Image source of the above article: Inovenso
Article Source: https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=4377