© Copyright 2020 Foshan Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Sitemap
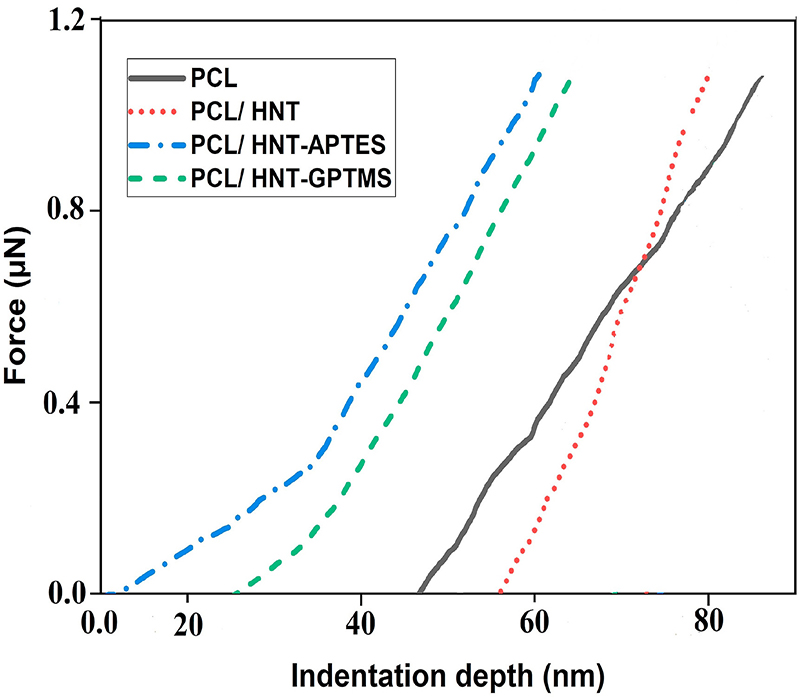
There is remarkable interest in the fabrication of polymeric composite nano/micro-fibers by electrospinning for many applications ranging from bioengineering to water/air filtration. In almost all of these applications, the mechanical properties of both the polymer fibers and their assemblies, are significant. In this study, unmodified, 3-Glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (GPTMS) or 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) modified halloysite clay nanotube (HNT) reinforced polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibers were successfully synthesized via the electrospinning. The morphology and mechanical features of the obtained electrospun fibers were investigated by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and AFM-based nanoindentation for single fibers in nanoscale, respectively. Besides, scanning electron microscopy and tensile strength tests were used to investigate whole fibrous structures in microscale. The AFMresults, accompanied by SEM and tensile strength, support the conclusion that silane-modification affected positively the morphology and mechanical characteristics of electrospun PCL nanofibers. Therefore, it was concluded that the morphological and mechanical features from the single fibers in the nanofiber mats were related to the whole fibrous structure.
通过静电纺丝制造聚合物复合纳米/微纤维引起了人们的极大兴趣,其应用范围涵盖从生物工程到水/空气过滤的许多应用。在几乎所有这些应用中,聚合物纤维及其组件的机械性能都很重要。在这项研究中,通过静电纺丝成功地合成了未改性的3-缩水甘油氧基丙基三甲氧基硅烷(GPTMS)或3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES)改性的埃洛石粘土纳米管(HNT)增强的聚己内酯(PCL)纳米纤维。分别通过原子力显微镜(AFM)和基于AFM的纳米压痕对单根纳米纤维进行了研究,研究了所得电纺纤维的形貌和力学性能。此外,使用扫描电子显微镜和拉伸强度测试来研究整个纤维结构的微观尺度。原子力显微镜(AFM)结果,连同扫描电镜(SEM)和拉伸强度,证明了以下结论:硅烷改性对电纺PCL纳米纤维的形态和机械特性产生积极影响。因此,可以得出结论,纳米纤维垫中单纤维的形态和力学特征与整个纤维结构有关。
Published: 2020
Journal :POLYMER TESTING
Impact Factor:3.781
Paper link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142941820321061